integration review
Integration review:
Defintions: Know these and be able to use them.
Riemann sum
Double integral
Area and volume as a double integral
Iterated integral
Type 1 and type 2 regions
Average value of a function on a region
first and second moments (about a line) of a function on a region
center of mass of a lamina, centroid of a region
Radius of gyration of a lamina about the y-axis (x-axis)
Triple integral
Volume as a triple integral
Line integrals with respect to arc length, x, y, or z (if the curve is a space curve)
Length as a line integral
vector field Force field
Work as a line integral
gradient field
conservative vector field
potential
Theorems: Know these their consequences
Linearity of double integrals (and triple integrals and line integrals).
Comparability of double integrals ( and triple integrals and line integrals)
Fubini's Theorem
Change of variables Theorem
Fundamental Theorem for line integrals
Characterization Theorem for conservative vector fields
Green's Theorem
Typical problems
16_12
Compute a Riemann sum for a function
Compute a Riemann sum for a table of values
Double integral as the limit of a Riemann sum.
Compute a double integral by realizing it as a volume
Use Fubini's Theorem to compute a double integral
Compute an iterated integral
Compute a volume using an iterated integral
Compute an average height
>
16_34
double integral trivia
compute a double integral over a type 1 or type 2
another compute a double integral over a type 1 or type 2
another compute a double integral over a type 1 or type 2
reverse the order of integration
convert to polar coordinates
compute a volume using polar coordinates
What's left after a hole is drilled in a sphere?
>
16_56
compute the center of mass of a triangular region with variable density
Find center of mass of quarter disk
Find radius of gyration of rectangle in first quadrant
compute the area of a plane which lies above a given triangle.
another compute a double integral over a type 1 or type 2
compute an area using polar coordinates
What's left after a hole is drilled in a sphere?
>
16_78
evaluate a triple iterated integral
compute an average temperature
compute an average temperature using cylindrical coordinates
compute a mass using spherical coordinates
y-coordinate of the center of mass.
Find average density of a prism
change of variable problem for double integrals
change of variable problem for triple integrals
17_12
identify a gradient field
Find the area of a fence. Find its average height
Find the mass and center of mass of a wire Find its average density.
Calculate line integrals with respect to x or y
Calculate a work integral along various paths from A to B
>
17_34
Calculate line integrals for gradient fields
Find potentials.
Calculate work integral using Green's theorem
Express area as line integral and evaluate.
Sample questions. More later in week .
1. Draw a picture of the region R for the integral
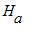 . Then reverse the order of integration and evaluate.
. Then reverse the order of integration and evaluate.
2. Find the average value of
![]() over the rectangular solid with opposite corners (0,0,0) and (1,2,3)
over the rectangular solid with opposite corners (0,0,0) and (1,2,3)
3. Let a > 0. Let
![]() be the solid below the plane
be the solid below the plane
![]() , above the xy-plane and inside the cylinder
, above the xy-plane and inside the cylinder
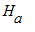 . Express the volume of
. Express the volume of
![]() as an iterated double integral in polar coordinates. Evaluate. Calculate the centroid of
as an iterated double integral in polar coordinates. Evaluate. Calculate the centroid of
![]() .
.
4. Find the maximum and minimum values M and m of
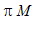 on the domain D = {(x,y)|
on the domain D = {(x,y)|
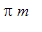 }. Then show that the integral of f over D is between
}. Then show that the integral of f over D is between
![]() and
and
![]()
5. Find the center of mass of the line segment from (0,1,0) to (2,0,1) if the density at each point on the wire is given by
![]() .
.
6. Show that the vector field F =<P,Q> = <
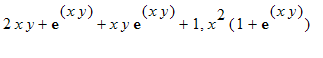 > is conservative. Use this to evaluate the work integral
> is conservative. Use this to evaluate the work integral
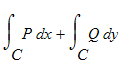 . over any nice curve C from (0,0) to (1,1).
. over any nice curve C from (0,0) to (1,1).
7. Obtain the formula for the area of a triangle with base b and height h by evaluating a line integral