Skip to main content\(\newcommand{\N}{\mathbb N}
\newcommand{\Z}{\mathbb Z}
\newcommand{\Q}{\mathbb Q}
\newcommand{\R}{\mathbb R}
\newcommand{\lt}{<}
\newcommand{\gt}{>}
\newcommand{\amp}{&}
\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}
\newcommand{\fillinmath}[1]{\mathchoice{\colorbox{fillinmathshade}{$\displaystyle \phantom{\,#1\,}$}}{\colorbox{fillinmathshade}{$\textstyle \phantom{\,#1\,}$}}{\colorbox{fillinmathshade}{$\scriptstyle \phantom{\,#1\,}$}}{\colorbox{fillinmathshade}{$\scriptscriptstyle\phantom{\,#1\,}$}}}
\)
Exercises 7.3 Practice Problems
1.
Suppose
\(f(x)=x^2-2\text{.}\) Compute the average rate of change of
\(f(x)\) from
\(x=1\) to
\(x=5\text{.}\)
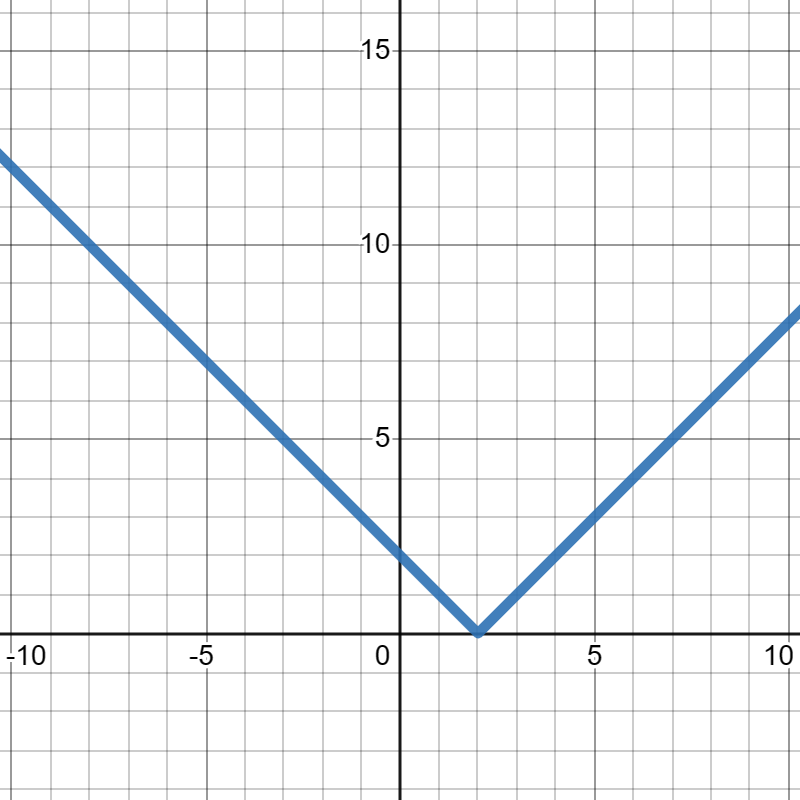
2.
Suppose
\(f(x)\) is given in the graph below. Compute the average rate of change of
\(f(x)\) from
\(x=-5\) to
\(x=2\text{.}\)
3.
Suppose
\(f(x)=x^2 +2x +3\text{.}\) Compute the average rate of change of
\(f(x)\) from
\(x=-1\) to
\(x=1\text{.}\)
4.
Suppose
\(g(x)\) is given in the table below. Compute the average rate of change of
\(g(x)\) from
\(x=1\) to
\(x=5\text{.}\)
Table 7.3.1.
| \(x\) |
\(1\) |
\(2\) |
\(3\) |
\(4\) |
\(5\) |
| \(g(x)\) |
\(0\) |
\(2\) |
\(4\) |
\(1\) |
\(0\) |
5.
Suppose
\(f(x)=\frac{x+3}{x-2}\text{.}\) Compute the average rate of change of
\(f(x)\) from
\(x=0\) to
\(x=4\text{.}\)
6.
Suppose
\(f(x)=x^3 + 5x\text{.}\) Compute the average rate of change of
\(f(x)\) from
\(x=-2\) to
\(x=2\text{.}\)
7.
Suppose
\(f(x)\) is given in the table below. Compute the average rate of change of
\(f(x)\) from
\(x=2\) to
\(x=5\text{.}\)
Table 7.3.2.
| \(x\) |
\(2\) |
\(4\) |
\(5\) |
\(7\) |
\(9\) |
| \(f(x)\) |
\(1\) |
\(-2\) |
\(4\) |
\(10\) |
\(0\) |
8.
Suppose
\(f(x)=x^2+16\text{.}\) Compute the average rate of change of
\(f(x)\) from
\(x=1\) to
\(x=10\text{.}\)
9.
Suppose
\(g(x)\) is given in the table below. Compute the average rate of change of
\(g(x)\) from
\(x=1\) to
\(x=7\text{.}\)
Table 7.3.3.
| \(x\) |
\(1\) |
\(3\) |
\(5\) |
\(7\) |
\(15\) |
| \(g(x)\) |
\(10\) |
\(2\) |
\(14\) |
\(21\) |
\(0\) |
10.
Suppose
\(f(x)=3x-7\text{.}\) Compute the average rate of change of
\(f(x)\) from
\(x=-5\) to
\(x=-2\text{.}\)
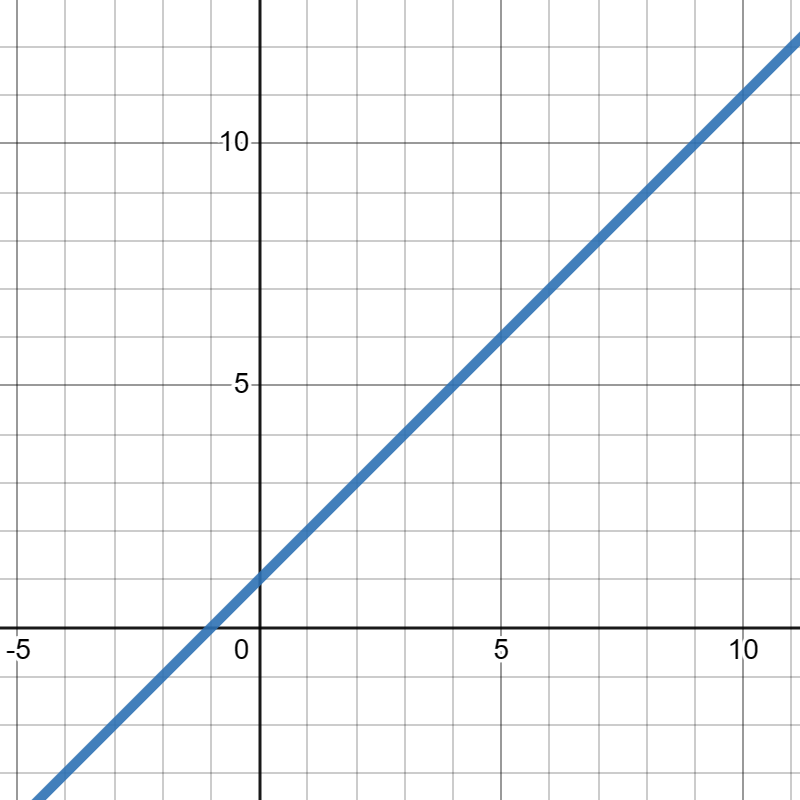
11.
Suppose
\(f(x)\) is given in the graph below. Compute the average rate of change of
\(f(x)\) from
\(x=0\) to
\(x=4\text{.}\)
12.
Suppose
\(f(x)=x^2-21\text{.}\) Compute the average rate of change of
\(f(x)\) from
\(x=3\) to
\(x=5\text{.}\)
13.
Suppose
\(f(x)=x^2-2\text{.}\) Compute the average rate of change of
\(f(x)\) from
\(x=1\) to
\(x=1+h\text{.}\)
14.
Suppose
\(f(x)=3x^2 +2x\text{.}\) Compute the average rate of change of
\(f(x)\) from
\(x=2\) to
\(x=2+h\text{.}\)
15.
Suppose
\(f(x)=10x+2\text{.}\) Compute the average rate of change of
\(f(x)\) from
\(x=a\) to
\(x=a+h\text{.}\)
16.
Suppose
\(f(x)=x^2 +4x +4\text{.}\) Compute the average rate of change of
\(f(x)\) from
\(x=a\) to
\(x=a+h\text{.}\)
17.
Suppose
\(f(x)=x^2+25\text{.}\) Compute the average rate of change of
\(f(x)\) from
\(x=5\) to
\(x=5+h\text{.}\)
18.
Suppose
\(f(x)=-x^2-3x+1\text{.}\) Compute the average rate of change of
\(f(x)\) from
\(x=a\) to
\(x=a+h\text{.}\)
19.
Suppose
\(f(x)=2x^2+10x\text{.}\) Compute the average rate of change of
\(f(x)\) from
\(x=3\) to
\(x=3+h\text{.}\)