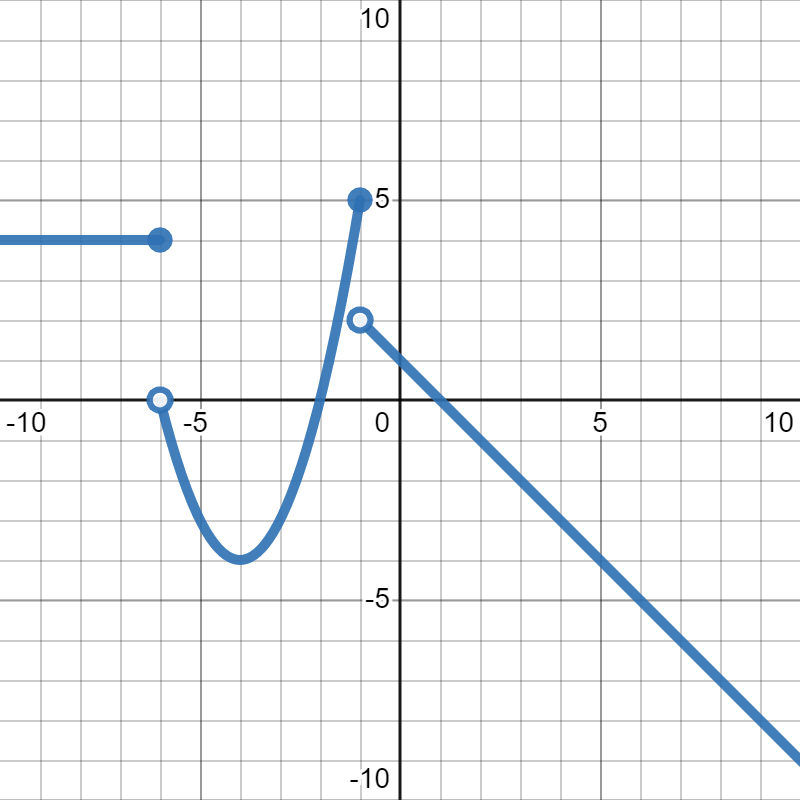
Suppose \(g(x)\) is given in the graph below:
Now, suppose we want to find \(g(-1)\text{.}\) We know that \(-1\) is our input, which is represented by the \(x\)-values on the graph. So, we move along the \(x\)-axis to where \(x=-1\text{.}\) Then, we look up and down at that \(x\)-value to see where the graph crosses it. Moving up, we see that the point \((-1,5)\) is on the graph. Since the \(y\)-values represent the outputs, that tells us that \(g(-1)=5\text{.}\)